Everyone knows that to have life on a world, you want three crucial objects: water, heat, and meals. Now add to {that a} issue referred to as “entropy”. It performs a job in figuring out if a given planet can maintain and develop advanced life.
Scientist Luigi Petraccone, a chemistry researcher on the College of Naples in Italy, checked out planetary entropy. He is eager about how scientists choose planets that might be liveable. He launched a paper that examines one thing referred to as “planetary entropy production” (PEP). Here is the way it works.
A liveable world wants a biosphere with stuff dwelling inside it. All life grows and expands, utilizing the obtainable water, heat, and meals sources. Because it seems, entropy performs out inside a world’s biosphere. And, it wants a comparatively excessive PEP.
That makes it extra prone to have advanced dwelling programs and means it could be a superb goal for exploration. And, in line with Petraccone’s paper, it does not matter what the chemical foundation for that life is—whether or not carbon, silicon, or another component. What issues is how life proceeds to higher complexity.

What’s Entropy?
Earlier than we dive into Petraccone’s paper, let’s speak about entropy. The dictionary definition in physics is: “a thermodynamic quantity representing the unavailability of a system’s thermal energy for conversion into mechanical work.”
The second regulation of thermodynamics requires that the universe strikes in a course wherein entropy will increase.
That appears slightly advanced, so let’s consider entropy as a measure of randomness or dysfunction in a system. An orderly system has precisely sufficient power to do the issues it must do.
If it produces (or good points) extra power, that will get expressed in the next state of entropy. Dwelling issues are extremely ordered and require a relentless enter of power to take care of a state of low entropy.
They produce waste and by-products and, after all, lose power as a part of the method of life. The extra power coming right into a system and subsequently misplaced by that system to its environment, the much less ordered and extra random issues get. Basically, the upper its entropy state turns into.
Entropy in biology comes into play if you have a look at the programs that contribute to life on a planet. Petraccone writes:
“The extent of entropy production is proportional to the ability of such systems to dissipate free energy and thus to ‘live’, to evolve, to grow in complexity. Generally, a certain threshold of entropy production must be exceeded for the emergence of complex self-organizing structures. Thus, the entropy production can be considered as the thermodynamic thrust that drives life emergence and evolution.”
That brings us to the “planetary entropy production” (PEP) worth that may assist scientists goal seemingly life-friendly planets.
Probably the most liveable ones shall be the place life can generate probably the most entropy. The extra advanced and dynamic the life kinds are, the extra entropy they will produce and the upper PEP worth they keep. Petraccone proposes that totally different planets may have roughly of an power potential, predicting which planets are more than likely to be liveable.
Making use of Planetary Entropy Manufacturing to a Life Search
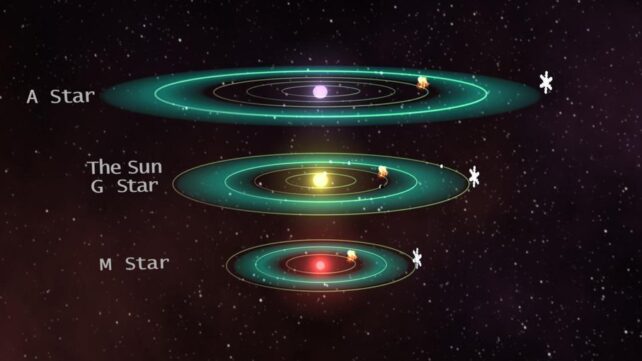
Determining the place and if life occurs on a planet is essential. First, it must be throughout the circumstellar liveable zone (CHZ) of its star. That is the place water can exist on the floor in a liquid state.
It additionally issues the place within the CHZ the planet orbits. If it is too near the within edge, it could lose no matter water it has on account of stellar heating (and a runaway greenhouse impact). If it is nearer to the surface edge, it won’t be as hospitable as one within the central space of the CHZ. As well as, a given planet could also be within the excellent a part of the zone however produce other challenges to supporting a biosphere.
Why not seek for planets all through the CHZ? There are thermodynamic variations between the internal and outer edges of the CHZ. The internal edge is extra advantageous for the event of advanced biospheres.
Each PEP and the obtainable free power for Earth-like planets improve with stellar temperature. With that data, Petraccone and his group utilized their calculations to guage the PEP and free power for a particular pattern of proposed liveable planets.
Scientists additionally want to determine the higher restrict to a world’s PEP worth and the corresponding free power it receives as a operate of stellar temperature and planetary orbital parameters.
Petraccone writes, for instance, that solely Earth-like planets within the CHZ of G and F stars can have a PEP worth larger than the Earth worth (Earth is what we use for comparability). Which means they’d be prone to assist life, versus planets in different components of the liveable zone.
Why Use PEP as a Rationale for Planetary Habitability?
Apparently, among the many just lately proposed liveable exoplanets, so-called “Hycean” worlds seem the thermodynamically finest candidates. These are planets with liquid water oceans and hydrogen-rich atmospheres. Our planet is an efficient instance and can be utilized as a “roadmap” to analysis.
Scientists are already studying the best mix of land to oceans for a habitable world, utilizing Earth as an analog. It lies near the internal fringe of the Solar’s CHZ, which places it in the correct place to have the next PEP worth.
If we assume Earth’s PEP worth is required for all times, then it permits planetary scientists to give you an “entropic habitable zone” (or EHZ). It contains the gap from a star the place a planet has liquid water plus a excessive PEP worth.
Apply these standards to planets, and it seems that worlds round low-mass stars would not develop a excessive sufficient EHZ to maintain life. Nor might M and Okay stars. Nonetheless, some fraction of worlds round F and G stars might land within the fortunate “zone” and proceed to develop life.
Deciding on These Doable Liveable Planets
Lately we see increasingly discoveries of exoplanets round close by stars. Inspecting all of them to seek for life is well-nigh not possible. So, scientists want some helpful standards to prioritize targets for examine.
Together with different elements, entropy manufacturing appears to be a superb indicator of whether or not or not a given world can host life—and the way advanced that life is.
Apparently, a significant benefit to utilizing PEP and presence within the EHZ as a approach to consider a world is that it does not require assumptions about its atmospheric situation. Nor do these elements indicate any conclusions in regards to the chemical foundation of the dwelling programs on any given world.
They merely present a means for scientists to fee a world as they sift by way of 1000’s of exoplanets for additional examine.
This text was initially revealed by Universe Today. Learn the original article.



