Mini brains grown in a lab from stem cells spontaneously developed rudimentary eye buildings, scientists reported in an enchanting paper in 2021.
On tiny, human-derived mind organoids grown in dishes, two bilaterally symmetrical optic cups had been seen to develop, mirroring the event of eye buildings in human embryos.
This unbelievable outcome will assist us to higher perceive the method of eye differentiation and improvement, in addition to eye illnesses.
“Our work highlights the remarkable ability of brain organoids to generate primitive sensory structures that are light sensitive and harbor cell types similar to those found in the body,” said neuroscientist Jay Gopalakrishnan of College Hospital Düsseldorf in Germany.
“These organoids can help to study brain-eye interactions during embryo development, model congenital retinal disorders, and generate patient-specific retinal cell types for personalized drug testing and transplantation therapies.”
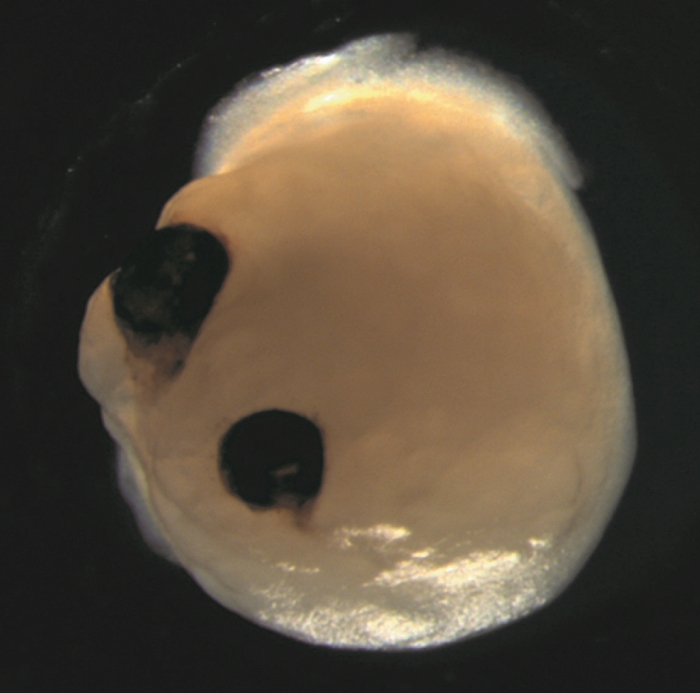
Mind organoids aren’t true brains, as you may be considering of them. They’re small, three-dimensional buildings grown from induced pluripotent stem cells – cells harvested from grownup people and reverse engineered into stem cells, which have the potential to develop into many several types of tissue.
On this case, these stem cells are coaxed to develop into blobs of mind tissue, with out something resembling ideas, feelings, or consciousness.
Such ‘mini brains’ are used for analysis functions the place utilizing precise residing brains can be inconceivable, or on the very least, ethically tough – testing drug responses, for instance, or observing cell improvement underneath sure opposed situations.
This time, Gopalakrishnan and his colleagues had been in search of to watch eye improvement.
In earlier analysis, different scientists had used embryonic stem cells to develop optic cups, the buildings that grow to be almost the entire globe of the eye throughout embryonic improvement. And different analysis had developed optic cup-like buildings from induced pluripotent stem cells.
Moderately than develop these buildings instantly, Gopalakrishnan’s crew needed to see in the event that they may very well be grown as an built-in a part of mind organoids. This could add the good thing about seeing how the 2 sorts of tissue can develop collectively, moderately than simply rising optic buildings in isolation.
“Eye development is a complex process, and understanding it could allow underpinning the molecular basis of early retinal diseases,” the researchers wrote in their paper.
“Thus, it is crucial to study optic vesicles that are the primordium of the eye whose proximal end is attached to the forebrain, essential for proper eye formation.”
Earlier work within the improvement of organoids confirmed proof of retinal cells, however these didn’t develop optic buildings, so the crew modified their protocols. They did not try to drive the event of purely neural cells on the early levels of neural differentiation, and added retinol acetate to the tradition medium as an help to eye improvement.
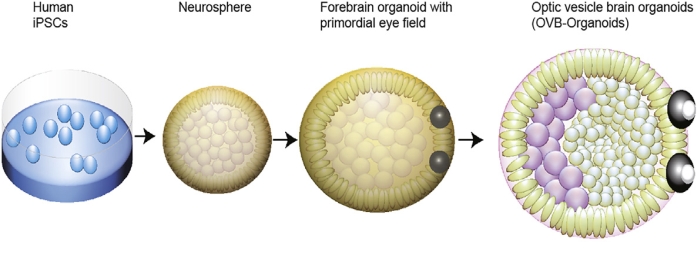
Their fastidiously tended child brains shaped optic cups as early as 30 days into improvement, with the buildings clearly seen at 50 days. That is per the timing of eye development in the human embryo, which implies these organoids may very well be helpful for learning the intricacies of this course of.
There are different implications, too. The optic cups contained totally different retinal cell sorts, which organized into neural networks that responded to mild, and even contained lens and corneal tissue. Lastly, the buildings displayed retinal connectivity to areas of the mind tissue.
“In the mammalian brain, nerve fibers of retinal ganglion cells reach out to connect with their brain targets, an aspect that has never before been shown in an in vitro system,” Gopalakrishnan said.
And it is reproducible. Of the 314 mind organoids the crew grew, 73 % developed optic cups. The crew hopes to develop methods for protecting these buildings viable on longer time-scales for performing extra in-depth analysis with enormous potential, the researchers mentioned.
“Optic vesicle-containing brain organoids displaying highly specialized neuronal cell types can be developed, paving the way to generate personalized organoids and retinal pigment epithelial sheets for transplantation,” they wrote in their paper.
“We believe that [these] are next-generation organoids helping to model retinopathies that emerge from early neurodevelopmental disorders.”
The analysis has been revealed in Cell Stem Cell.
A model of this text was first revealed in August 2021.



