November 29, 2023
3 min learn
A photo voltaic outburst shoots charged particles into area—and towards Earth
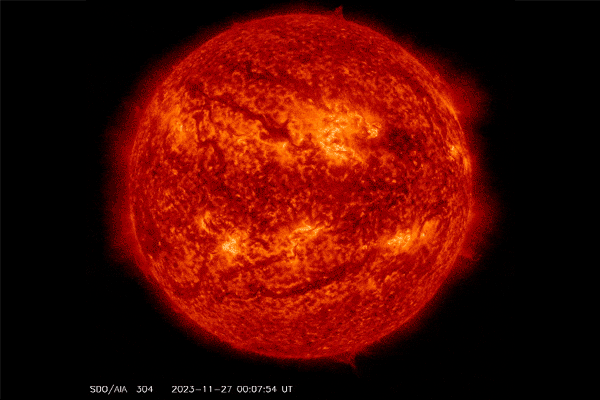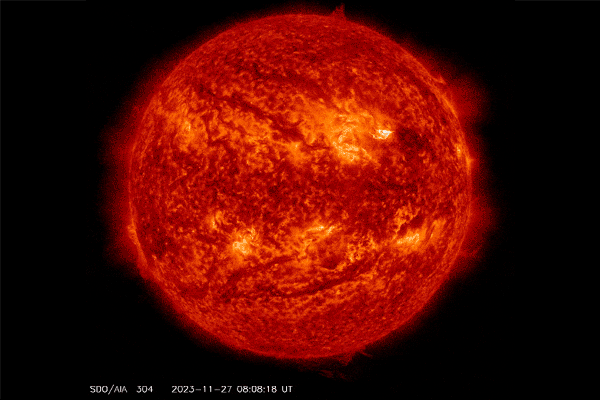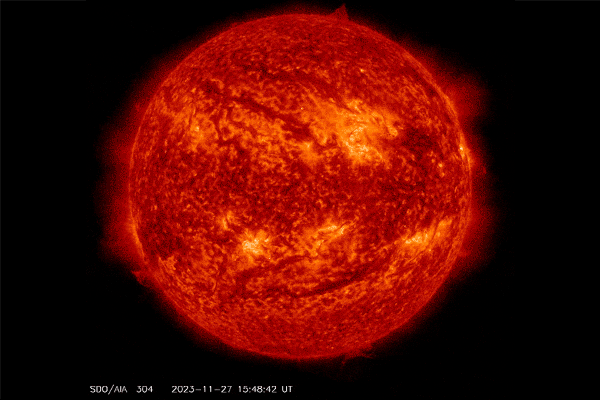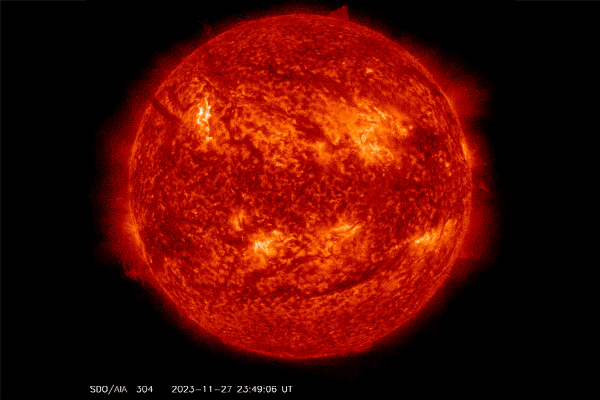
A filament erupted from the solar on Nov. 27, 2023, and left a “canyon of fire” seen within the backside proper of this view.
A protracted filament of roiling plasma arcing over the solar’s floor snapped this week, forsaking a scalding scar that has been dubbed a “canyon of fire.” It additionally spat a burst of photo voltaic plasma into area. There’s an opportunity this photo voltaic outburst and a number of other that adopted it might set off minor geomagnetic storms on Earth.
The photo voltaic spectacle befell at midnight EST on November 27, in accordance with the sun-monitoring web site SpaceWeather.com. The canyon of fireplace remained within the solar’s soup of plasma, which is materials so sizzling that it has misplaced all its electrons. This canyon of vivid plasma traced the magnetic area line that had anchored the filament in place.
The canyon impact happens as a result of a filament is an arc of cooler, darker plasma that’s anchored into the sun’s magnetic field on every finish. When a filament erupts, the arc shatters into area, ripping freed from the solar’s magnetic area to disclose a glowing scar of hotter, brighter plasma the place that magnetic area line ran. (Filaments are typically referred to as prominences once they happen alongside the sting of the solar, as seen from Earth, coming out as vivid, wispy arcs towards the blackness of area.)
The latest damaged filament additionally triggered a coronal mass ejection (CME), scientist communicate for a blob of plasma that the solar shoots into area. (In distinction, solar flares, one other frequent kind of outburst, are made up of radiation.) The CME was joined hours later by at the very least two extra, in accordance with SpaceWeather.com. And one in every of these was directed in the identical normal route because the filament-triggered eruption, in accordance with the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Area Climate Prediction Middle.
As soon as the plasma materials makes its means nearer to us, it might disrupt Earth’s magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble surrounding our planet. This disruption is named a geomagnetic storm. NOAA has famous that it expects that simply minor geomagnetic storms could outcome as soon as the fabric makes its means towards Earth on November 30. Robust geomagnetic storms can paint the poles with auroras, however they’ll additionally interrupt satellite-based navigation programs and energy grids on the floor.
Photo voltaic exercise is ruled by our solar’s 11-year cycle, which is intimately related to its self-generated magnetic area. At present, the solar’s magnetic poles are disappearing, heralding the height of the photo voltaic exercise cycle. Within the coming years, as our star’s magnetic area rebuilds itself, photo voltaic exercise—which is measured by tallies of the chilly, darkish sunspots that mar the solar’s floor—will ebb, and the following photo voltaic minimal, anticipated on the flip of the last decade, will start.
Scientists make use of a bunch of instruments to observe the solar. Because the mid-1700s, astronomers have monitored sunspots with telescopes; NASA’s Photo voltaic Dynamics Observatory spacecraft, which captured the footage of the brand new damaged filament included on this article, launched in 2010.
However as heliophysicists search to know how our star works, they’ve developed a trio of highly effective new devices which might be gathering unprecedented observations this photo voltaic cycle: NASA’s Parker Photo voltaic Probe, which launched in 2018 and has flown nearer to the solar than every other human-made object; the European Area Company’s Photo voltaic Orbiter, which launched in 2020 and can let scientists peer on the solar’s poles; and the Daniel Okay. Inouye Photo voltaic Telescope in Hawaii, which produced its first pictures in 2020 and has given researchers an in depth view of our dwelling star’s magnetic exercise. The mixture, scientists hope, will enable them to begin predicting in earnest how the sun’s activity influences life on Earth.



