December 5, 2023
3 min learn
A large iceberg referred to as A23a, which broke off from Antarctica in 1986, is lastly shifting away from the icy continent after being caught on the seafloor for many years
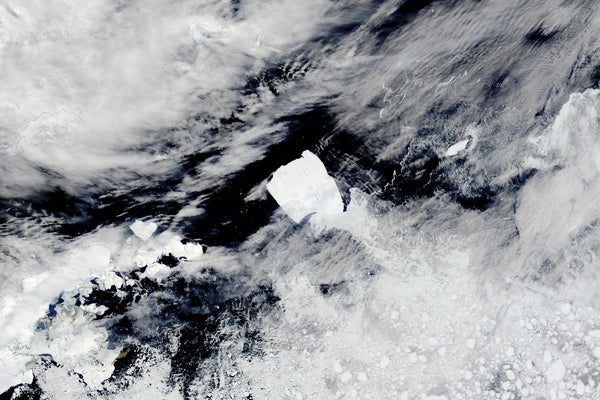
Caught on the seafloor for many years, Iceberg A-23A now freely drifts northward towards hotter, iceberg-destroying waters.
The world’s largest iceberg, A23a, is on the transfer after being trapped in place off Antarctica’s shoreline for nearly 40 years. The large “ice island,” which is 3 times the dimensions of New York Metropolis, will probably drift into the “iceberg graveyard,” probably placing it on a collision course with an vital penguin refuge earlier than it fractures and melts away.
The berg, which has a floor space of round 1,550 sq. miles (4,000 sq. kilometers), was initially birthed in 1986 when it calved from the Filchner Ice Shelf. However the hefty berg acquired caught quickly after when its submerged keel turned lodged on the seafloor within the Weddell Sea.
A23a has held the title of the world’s largest iceberg on a number of events as different, extra huge ice slabs got here and went whereas it sat in place, Christopher Shuman, a glaciologist on the College of Maryland and NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle, advised Stay Science in an electronic mail.
The aged ice mass most lately regained its title in June, when the earlier record-holder A76a ripped apart after being flung toward the equator by ocean currents.
On Nov. 25, main information shops reported that A23a had lastly began to maneuver. Nevertheless, the berg’s bid for freedom really started in 2020 when it began to develop into unstuck from its seafloor tether, the BBC reported.
Satellite tv for pc imagery shared on X (previously often called Twitter) by the British Antarctic Survey reveals that A23a lastly started shifting from its sticking level in January this yr. It has since traveled a whole lot of miles alongside Antarctica’s shoreline.
A23a turned caught because of the thickness of its ice. Icebergs of this dimension might be as much as 1,300 toes (400 meters) tall from prime to backside, with round 90% of its mass submerged, Shuman mentioned.
Being caught in place for many years is “not uncommon” for icebergs of this dimension, Shuman mentioned. Early Antarctic explorers referred to them as “ice islands,” he added.
These trapped bergs are capable of keep most of their ice mass as a result of they’re so giant and keep near Antarctica. It’s unclear how a lot water is trapped contained in the berg, however A68 — one other former world’s largest iceberg, which was across the identical dimension as A23a is now — dumped more than 1 trillion tons of water into the ocean throughout its lifetime.
A23a probably turned unstuck as ice on its underside melted from under, which diminished its weight and lifted it off the seafloor. This ultimately occurs to all stranded icebergs and was probably not associated to local weather change, the BBC reported.
A23a will probably be pushed north by ocean currents into the Drake Passage, often known as the iceberg graveyard — a physique of water that almost all different giant icebergs born into the Weddell Sea, together with A76a and A68a, have handed by means of on their gradual marches to their watery graves.
This space comprises a number of islands that the bergs can occasionally bump into, together with South Georgia — an inhabited island within the Southern Ocean that’s residence to huge penguin colonies. In 2020, A68a was on a collision course with South Georgia, which significantly involved scientists on account of its potential for disrupting the penguins’ feeding capabilities. Nevertheless, the berg narrowly prevented the island earlier than fracturing into more than a dozen of smaller pieces.
South Georgia might be in A23a’s path, elevating fears of one other doable collision sooner or later. However this “isn’t a certainty,” Shuman mentioned.
If A23a misses South Georgia, its dimension might imply it survives as far north as South Africa, the place it might majorly affect delivery routes, researchers told Reuters. Nevertheless, Shuman believes that fracture traces within the berg might make it extra prone to breaking up earlier than it will get this far.
Scientists will proceed to trace the iceberg’s actions to slim down the place it could go subsequent.
Copyright 2023 LiveScience, a Future firm. All rights reserved. This materials is probably not printed, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.



